EV Charging Stations: How Do They Work?
Electric vehicles (EVs) have made driving cleaner and better for the earth. Millions of people have switched to electric cars in the last few years to reduce smog and gas costs. Charging electric vehicles quickly is more important than ever as more people buy them.
The rise of the market for electric cars depends on where to charge them. These sites also give people with electric vehicles more faith in moving to them. This article explains what EV charging sites are, how they work, and the different types of chargers (AC and DC).
What Is An Electric Vehicle Charger?
There are now more places to charge electric cars (EVs) at homes, parking lots, and gas stops. It’s all part of making the world a better place. You might be driving an electric car sooner than you think because the UK government won’t let people buy new gasoline or diesel cars after 2030. When an EV charger is plugged into a wall or the grid, it sends power to an electric vehicle. This is like plugging your phone into the wall to charge it.
New rules from the UK government in 2022 required innovative charge points for private car charging. This meant they had to be able to send and receive information and have a screen or a changeable user interface. It is against the rules for anyone or any business to sell, give, rent, lend, lease, or market a charge point for sale.
How To Use Charging Stations For Electric Vehicles
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) charges the batteries in electric cars. Let’s break them down to understand them better:
- Power: A place to charge electric vehicles is like a gas stop for them. A gas station needs oil, and an electric shop needs a place to get power. Most of this power comes from the primary power source, where your home gets power. Setting up a long cord to charge your car is like that.
- Conversion: Grid energy is like the power from your TV and phone. AC stands for changing current. Most electric cars need DC power to charge their batteries. The EV charger has a transformer that converts AC energy to DC electricity that your car’s battery can use.
A charging station for electric cars mostly takes power from the grid, like a plug in your house, and changes it into a form that your car’s battery can use.
Different Types Of Electric Charging Stations
There are different types of charging stations on the market, and each one can charge at a different speed and be used for other things:
- Level 1 Charging (240V AC): The most accessible chargers plug into 240V AC outlets in your home. Since they charge slowly, you can leave them to charge overnight at home. But you can’t use them on your phone while going fast. Charge stations at Level 1 can power 4-wheelers, 3-wheelers, and 2-wheelers with less than 3.5 kW.
- Level 2 Charging (380–400V AC): Level 2 chargers are better than Level 1 chargers. They can be found in homes, businesses, and public charging points. Level 2 chargers are great for everyday use because they charge quickly. Level 2 EV charging points can charge cars with four, three, or two wheels and produce 22 kW of power.
- Level 3 Charging (DC Fast): Direct current (DC) fast chargers send power straight to the car’s battery without change happening on board. Because they can quickly give a lot of energy and charge an EV to 80%, they are suitable for long trips and quick charging. This fast charging station can only work with four-wheelers and send out up to 400 kW of power.
Understanding How Electric Vehicles Are Charged
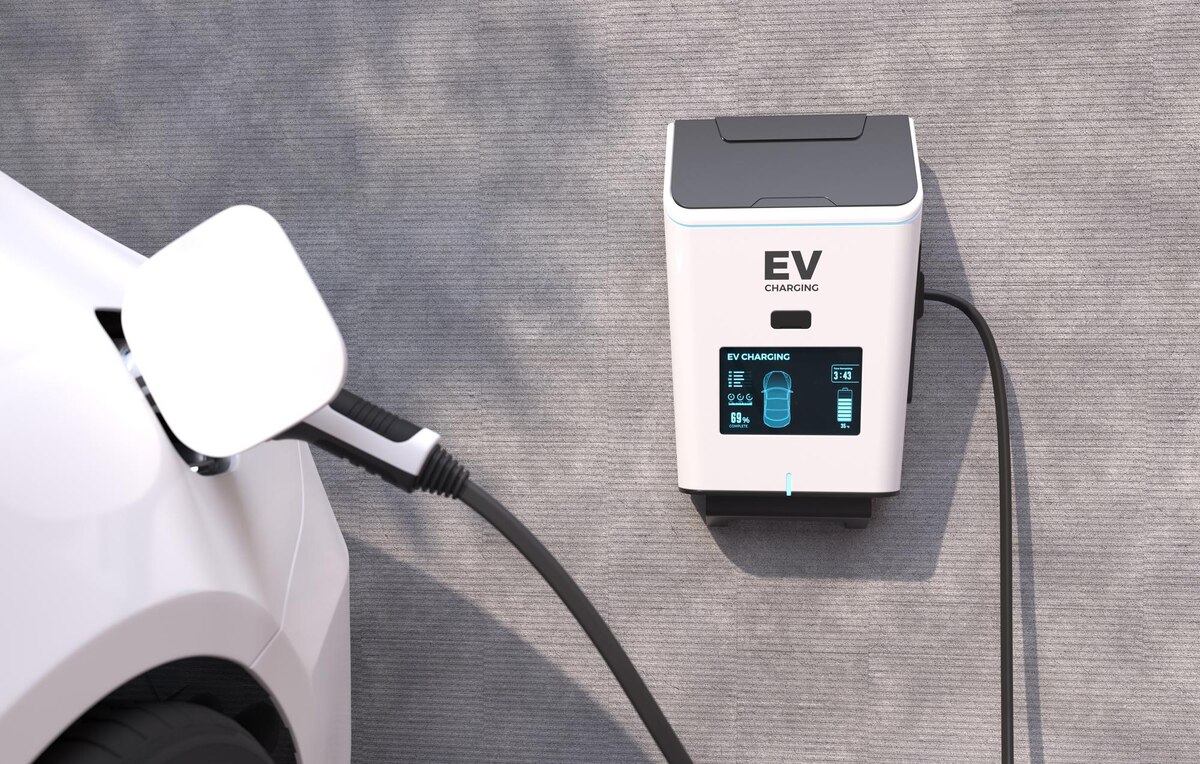
Putting the car on the EV charger at the charging station starts the charging process. This is how it usually works:
- Verification: Many charging stations need you to show an actual card, an app on your phone, or a way to pay wirelessly, like Static Wallet, to prove who you are. This ensures that only the right people can use the charging port and keeps it safe.
- Information sharing: The EV charger talks to the electric car to set the charging parameters, such as the speed, power, and current. This makes sure it’s safe and easy to charge.
- Charging: The charging station properly charges the electric vehicle’s battery by providing the correct amount of electricity and current. The battery stores the power so it can be used later. The charging station’s screen or a phone app will usually tell you how much power is left.
- Autocut: When the battery reaches a certain charge level, EV chargers can stop charging immediately, or the user can set their stop level. The charger has safety measures to prevent it from overcharging and setting fire to itself.
How Long Does It Take To Charge The Battery Fully In An Electric Car?
How long it takes to charge an electric car depends on the size of the battery, how fast it charges, and how much it is charged. A 7kW charging point can fully charge a 60kWh electric car in eight hours. It can be charged in 12 hours or 30 minutes.
What Does It Cost To Charge An Electric Vehicle?
It can cost more or less depending on where and what kind of charger you use. At 28p/kWh, a fully charged electric car at home can cost between £6 and £15. There will be free and paid public places. However, it’s generally accessible to charge an EV at work.
People need to know about the different ways to charge their cars and how much each one costs to make smart decisions and fully understand the financial benefits of moving to electric cars. So, when people try to figure out how much it usually costs to charge an electric car, they should consider a few things.
Conclusion
Many people who buy electric cars need places to charge them. Charging an electric car’s battery is simple and quick, whether at home, work or on the road. As technology improves, the system for charging electric vehicles will likely get faster, more flexible, and easier to use.